Variables
This section of the user guide describes how to assign and visualize variables with math expressions.
The Let Expression
The let expression sets variables and returns the value of the last variable by default.
The output of any streaming expression or math expression can be set to a variable.
Below is a simple example setting three variables a, b,
and c.
Variables a and b are set to arrays.
The variable c is set to the output of the ebeAdd function which performs element-by-element addition of the two arrays.
let(a=array(1, 2, 3),
b=array(10, 20, 30),
c=ebeAdd(a, b))In the response, notice that the last variable, c, is returned:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"c": [
11,
22,
33
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 4
}
]
}
}Echoing Variables
All variables can be output by setting the echo variable to true.
let(echo=true,
a=array(1, 2, 3),
b=array(10, 20, 30),
c=ebeAdd(a, b))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"a": [
1,
2,
3
],
"b": [
10,
20,
30
],
"c": [
11,
22,
33
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}A specific set of variables can be echoed by providing a comma-delimited list of variables to the echo parameter.
Because variables have been provided, the true value is assumed.
let(echo="a,b",
a=array(1, 2, 3),
b=array(10, 20, 30),
c=ebeAdd(a, b))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"a": [
1,
2,
3
],
"b": [
10,
20,
30
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}Visualizing Variables
The let expression can also include a zplot expression that can be used to visualize the variables.
In the example below the variables a and b are set to arrays.
The zplot function outputs the variables as x and y fields in the output.
let(a=array(1, 2, 3),
b=array(10, 20, 30),
zplot(x=a, y=b))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"x": 1,
"y": 10
},
{
"x": 2,
"y": 20
},
{
"x": 3,
"y": 30
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}Using this approach variables can be visualized using Zeppelin-Solr. In the example below the arrays are shown in table format.
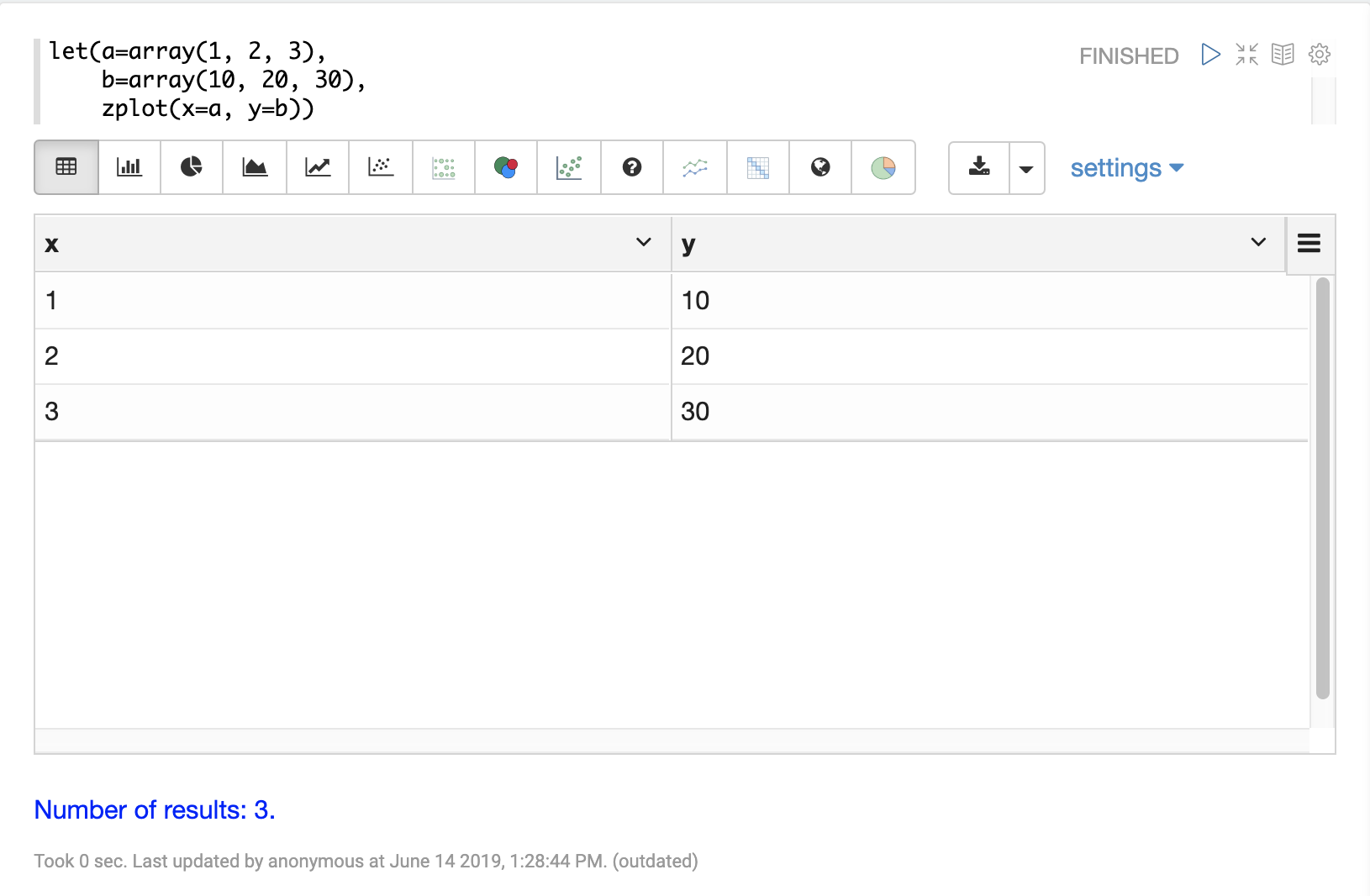
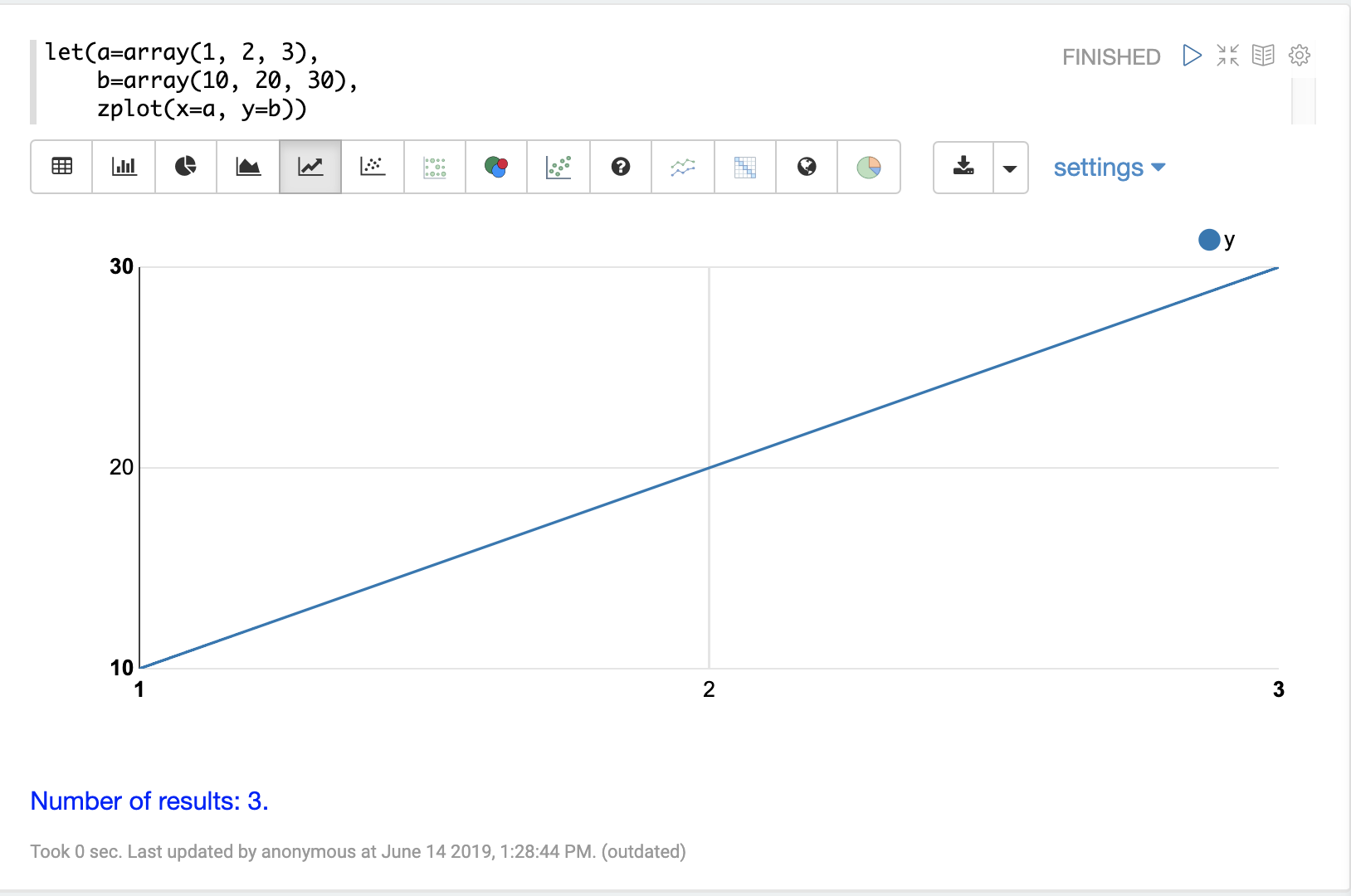
Once in table format we can plot the variables using one of the plotting or charting visualizations. The example below shows variables plotted on a line chart:
Caching Variables
Variables can be cached in-memory on the Solr node where the math expression was run. A cached variable can then be used in future expressions. Any object that can be set to a variable, including data structures and mathematical models, can be cached in-memory for future use.
The putCache function adds a variable to the cache.
In the example below an array is cached in the workspace workspace1 and bound to the key key1.
The workspace allows different users to cache objects in their own workspace.
The putCache function returns the variable that was added to the cache.
let(a=array(1, 2, 3),
b=array(10, 20, 30),
c=ebeAdd(a, b),
d=putCache(workspace1, key1, c))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"d": [
11,
22,
33
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 11
}
]
}
}The getCache function retrieves an object from the cache by its workspace and key.
In the example below the getCache function retrieves the array that was cached above and assigns it to variable a.
let(a=getCache(workspace1, key1))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"a": [
11,
22,
33
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 11
}
]
}
}The listCache function can be used to list the workspaces or the keys in a specific workspace.
In the example below listCache returns all the workspaces in the cache as an array of strings.
let(a=listCache())When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"a": [
"workspace1"
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}In the example below all the keys in a specific workspace are listed:
let(a=listCache(workspace1))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"a": [
"key1"
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}The removeCache function can be used to remove a key from a specific workspace.
The removeCache function removes the key from the cache and returns the object that was removed.
In the example below the array that was cached above is removed from the cache.
let(a=removeCache(workspace1, key1))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"a": [
11,
22,
33
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}