Monitoring with Prometheus and Grafana
If you use Prometheus and Grafana for metrics storage and data visualization, Solr includes a Prometheus exporter to collect metrics and other data.
The Prometheus exporter is included with the full Solr distribution, and is located under prometheus-exporter/.
It is not included in the slim Solr distribution.
A Prometheus exporter (solr-exporter) allows users to monitor not only Solr metrics which come from the Metrics API, but also facet counts which come from Faceting and responses to Collections API commands and Ping requests.
This graphic provides a more detailed view:
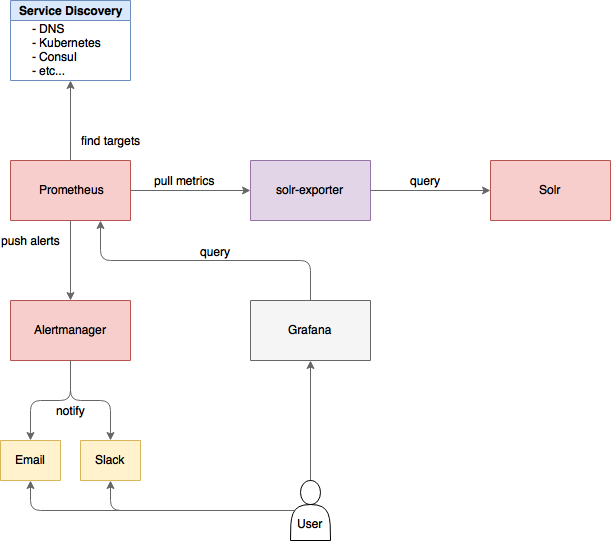
There are three aspects to running solr-exporter:
-
Modify the
solr-exporter-config.xmlto define the data to collect. Solr has a default configuration you can use, but if you would like to modify it before running the exporter the first time, see the section Exporter Configuration below. -
Start the exporter from within Solr. See the section below Starting the Exporter.
-
Modify your Prometheus configuration to listen on the correct port. See the section below Prometheus Configuration
Starting the Exporter
You can start solr-exporter by running ./bin/solr-exporter (Linux) or .\bin\solr-exporter.cmd (Windows) from the prometheus-exporter/ directory.
The metrics exposed by solr-exporter can be seen at the metrics endpoint: http://localhost:8983/solr/admin/metrics.
See the commands below depending on your operating system and Solr operating mode:
Linux
$ cd prometheus-exporter
$ ./bin/solr-exporter -p 9854 -b http://localhost:8983/solr -f ./conf/solr-exporter-config.xml -n 8$ cd prometheus-exporter
$ ./bin/solr-exporter -p 9854 -z localhost:2181/solr -f ./conf/solr-exporter-config.xml -n 16Windows
> cd prometheus-exporter
> .\bin\solr-exporter.cmd -p 9854 -b http://localhost:8983/solr -f .\conf\solr-exporter-config.xml -n 8> cd prometheus-exporter
> .\bin\solr-exporter -p 9854 -z localhost:2181/solr -f .\conf\solr-exporter-config.xml -n 16Command Line Parameters
The list of available parameters for the Prometheus Exporter. All parameters can be provided via an environment variable, instead of through the command line.
h,--help-
Optional
Default: none
Displays command line help and usage.
-p,--port,$PORT-
Optional
Default:
8989The port where Prometheus will listen for new data. This port will be used to configure Prometheus. It can be any port not already in use on your server.
-b,--baseurl,$SOLR_URL-
Optional
Default: see description
The Solr base URL (such as
http://localhost:8983/solr) when Solr is running in a user-managed cluster or a single-node installation. If you are running SolrCloud, do not specify this parameter. If neither the-bparameter nor the-zparameter are defined, the default is-b http://localhost:8983/solr. -z,--zkhost,$ZK_HOST-
Optional
Default: see description
The ZooKeeper connect string (such as
localhost:9983, orlocalhost:2181/solr) when Solr is running SolrCloud. If you are running a user-managed cluster or single-node installation, do not specify this parameter. If neither the-bparameter nor the-zparameter are defined, the-bparameter default is used. -f,--config-file,$CONFIG_FILE-
Optional
Default:
prometheus-exporter/conf/solr-exporter-config.xmlThe path to the configuration file that defines the Solr metrics to read.
-n,--num-threads,$NUM_THREADS-
Optional
Default:
1The number of threads. The
solr-exportercreates thread pools for requests to Solr. Request latency can be improved by increasing the number of threads. -s,--scrape-interval,$SCRAPE_INTERVAL-
Optional
Default:
60secondsThe number of seconds between collecting metrics from Solr. The
solr-exportercollects metrics from Solr every few seconds controlled by this setting. These metrics are cached and returned regardless of how frequently prometheus is configured to pull metrics from this tool. The freshness of the metrics can be improved by reducing the scrape interval but do not set it to a very low value because metrics collection can be expensive and can execute arbitrary searches to ping Solr. -i,--cluster-id,$CLUSTER_ID-
Optional
Default: see description
A unique ID for the cluster to monitor. This ID will be added to all metrics as a label
cluster_idand can be used as a filter in the Grafana dashboard if you operate multiple Solr clusters reporting to the same Prometheus instance. If this option is omitted, a hash of thebaseUrlorzkHostwill be used as ID by default. -u,--credentials,$CREDENTIALS-
Optional
Default: none
Specify the credentials in the format
username:password. Example:--credentials solr:SolrRocks.
Environment Variable Options
The ./bin scripts provided with the Prometheus Exporter support the use of custom java options through the following environment variables:
JAVA_HEAP-
Optional
Default:
512mSets the initial (
Xms) and max (Xmx) Java heap size. JAVA_MEM-
Optional
Default: none
Custom java memory settings (e.g.,
-Xms1g -Xmx2g). This is ignored ifJAVA_HEAPis provided. GC_TUNE-
Optional
Default:
-XX:+UseG1GCCustom Java garbage collection settings.
JAVA_OPTS-
Optional
Default: none
Extra JVM options.
ZK_CREDS_AND_ACLS-
Optional
Default: none
Credentials for connecting to a ZooKeeper host that is protected with ACLs. For more information on what to include in this variable, refer to the section ZooKeeper ACLs in Solr Scripts or the example Getting Metrics from a Secured SolrCloud below.
CLASSPATH_PREFIX-
Optional
Default: none
Location of extra libraries to load when starting the
solr-exporter.
All Command Line Parameters are able to be provided via environment variables when using the ./bin scripts.
Getting Metrics from a Secured SolrCloud
Your SolrCloud security configuration can be injected into solr-exporter using environment variables in a fashion similar to other clients using SolrJ.
This is possible because the main script picks up Environment Variable Options and passes them on to the Java process.
The following example assumes a SolrCloud instance secured by Basic Authentication Plugin, SSL and ZooKeeper Access Control.
Suppose you have a file basicauth.properties with the Solr Basic-Auth credentials:
httpBasicAuthUser=myUser httpBasicAuthPassword=myPassword
Then you can start the Exporter as follows (Linux).
$ cd prometheus-exporter
$ export JAVA_OPTS="-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=truststore.p12 -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=truststorePassword -Dsolr.httpclient.builder.factory=org.apache.solr.client.solrj.impl.PreemptiveBasicAuthClientBuilderFactory -Dsolr.httpclient.config=basicauth.properties"
$ export ZK_CREDS_AND_ACLS="-DzkCredentialsProvider=org.apache.solr.common.cloud.VMParamsSingleSetCredentialsDigestZkCredentialsProvider -DzkDigestUsername=readonly-user -DzkDigestPassword=zkUserPassword"
$ export CLASSPATH_PREFIX="../server/solr-webapp/webapp/WEB-INF/lib/commons-codec-1.11.jar"
$ ./bin/solr-exporter -p 9854 -z zk1:2181,zk2:2181,zk3:2181 -f ./conf/solr-exporter-config.xml -n 16- NOTE
-
The Exporter needs the
commons-codeclibrary for SSL/BasicAuth, but does not bring it. Therefore the example reuses it from the Solr web app. Of course, you can use a different source.
Exporter Configuration
The configuration for the solr-exporter defines the data to get from Solr.
This includes the metrics, but can also include queries to the PingRequestHandler, the Collections API, and a query to any query request handler.
A default example configuration is in prometheus-exporter/conf/solr-exporter-config.xml.
Below is a slightly shortened version of it:
<config>
<rules>
<ping>
<lst name="request">
<lst name="query">
<str name="path">/admin/ping</str>
</lst>
<arr name="jsonQueries">
<str>
. as $object | $object |
(if $object.status == "OK" then 1.0 else 0.0 end) as $value |
{
name : "solr_ping",
type : "GAUGE",
help : "See following URL: https://solr.apache.org/guide/solr/latest/deployment-guide/ping.html",
label_names : [],
label_values : [],
value : $value
}
</str>
</arr>
</lst>
</ping>
<metrics>
<lst name="request">
<lst name="query">
<str name="path">/admin/metrics</str>
<lst name="params">
<str name="group">all</str>
<str name="type">all</str>
<str name="prefix"></str>
<str name="property"></str>
</lst>
</lst>
<arr name="jsonQueries">
<!--
jetty metrics
-->
<str>
.metrics["solr.jetty"] | to_entries | .[] | select(.key | startswith("org.eclipse.jetty.server.handler.DefaultHandler")) | select(.key | endswith("xx-responses")) as $object |
$object.key | split(".") | last | split("-") | first as $status |
$object.value.count as $value |
{
name : "solr_metrics_jetty_response_total",
type : "COUNTER",
help : "See following URL: https://solr.apache.org/guide/solr/latest/deployment-guide/metrics-reporting.html",
label_names : ["status"],
label_values : [$status],
value : $value
}
</str>
...
</arr>
</lst>
</metrics>
<collections>
<lst name="request">
<lst name="query">
<str name="path">/admin/collections</str>
<lst name="params">
<str name="action">CLUSTERSTATUS</str>
</lst>
</lst>
<arr name="jsonQueries">
<str>
.cluster.live_nodes | length as $value|
{
name : "solr_collections_live_nodes",
type : "GAUGE",
help : "See following URL: https://solr.apache.org/guide/solr/latest/deployment-guide/cluster-node-management.html#clusterstatus",
label_names : [],
label_values : [],
value : $value
}
</str>
...
</arr>
</lst>
</collections>
<search>
<lst name="request">
<lst name="query">
<str name="collection">collection1</str>
<str name="path">/select</str>
<lst name="params">
<str name="q">*:*</str>
<str name="start">0</str>
<str name="rows">0</str>
<str name="json.facet">
{
category: {
type: terms,
field: cat
}
}
</str>
</lst>
</lst>
<arr name="jsonQueries">
<str>
.facets.category.buckets[] as $object |
$object.val as $term |
$object.count as $value |
{
name : "solr_facets_category",
type : "GAUGE",
help : "Category facets",
label_names : ["term"],
label_values : [$term],
value : $value
}
</str>
</arr>
</lst>
</search>
</rules>
</config>Configuration Tags and Elements
The solr-exporter works by making a request to Solr according to the definitions in the configuration file, scraping the response, and converting it to a JSON structure Prometheus can understand.
The configuration file defines the elements to request, how to scrape them, and where to place the extracted data in the JSON template.
The solr-exporter configuration file always starts and closes with two simple elements:
<config>
<rules>
</rules>
</config>Between these elements, the data the solr-exporter should request is defined.
There are several possible types of requests to make:
<ping>
|
Scrape the response to a Ping request. |
<metrics>
|
Scrape the response to a Metrics API request. |
<collections>
|
Scrape the response to a Collections API request. |
<search>
|
Scrape the response to a query request. |
Within each of these types, we need to define the query and how to work with the response. To do this, we define two additional elements:
<query>-
Defines the query parameter(s) used for the request. This section uses several additional properties to define your query:
collection-
Optional
Default: none
The collection to issue the query against. Only used with SolrCloud clusters.
core-
Optional
Default: none
The core to issue the query against. Only used with user-managed clusters or single-node installations.
path-
Optional
Default: none
The path to the query endpoint where the request will be sent. Examples include
admin/metricsor/selectoradmin/collections. params-
Optional
Default: none
Additional query parameters. These will vary depending on the request type and the endpoint. For example, if using the Metrics endpoint, you can add parameters to limit the query to a certain group and/or prefix. If you’re using the Collections API, the command you want to use would be a parameter.
<jsonQueries>-
This is an array that defines one or more JSON Queries in jq syntax. For more details about how to structure these queries, see the jq user manual.
A jq query has to output JSON in the following format:
{ "name": "solr_ping", "type": "GAUGE", "help": "See following URL: https://solr.apache.org/guide/solr/latest/deployment-guide/ping.html", "label_names": ["base_url","core"], "label_values": ["http://localhost:8983/solr","collection1"], "value": 1.0 }
See the section Exposition Format below for information about what information should go into each property, and an example of how the above example is translated for Prometheus.
Exposition Format
The solr-exporter converts the JSON to the following exposition format:
# TYPE <name> <type>
# HELP <name> <help>
<name>{<label_names[0]>=<label_values[0]>,<label_names[1]>=<labelvalues[1]>,...} <value>The following parameters should be set:
name-
The metric name to set. For more details, see Prometheus naming best practices.
type-
The type of the metric, can be
COUNTER,GAUGE,SUMMARY,HISTOGRAMorUNTYPED. For more details, see Prometheus metric types. help-
Help text for the metric.
label_names-
Label names for the metric. For more details, see Prometheus naming best practices.
label_values-
Label values for the metric. For more details, see Prometheus naming best practices.
value-
Value for the metric. Value must be set to Double type.
For example, solr-exporter converts the JSON in the previous section to the following:
# TYPE solr_ping gauge
# HELP solr_ping See following URL: https://solr.apache.org/guide/solr/latest/deployment-guide/ping.html
solr_ping{base_url="http://localhost:8983/solr",core="collection1"} 1.0Prometheus Configuration
Prometheus is a separate server that you need to download and deploy. More information can be found at the Prometheus Getting Started page.
In order for Prometheus to know about the solr-exporter, the listen address must be added to the Prometheus server’s prometheus.yml configuration file, as in this example:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'solr'
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:9854']If you already have a section for scrape_configs, you can add the job_name and other values in the same section.
When you apply the settings to Prometheus, it will start to pull Solr’s metrics from solr-exporter.
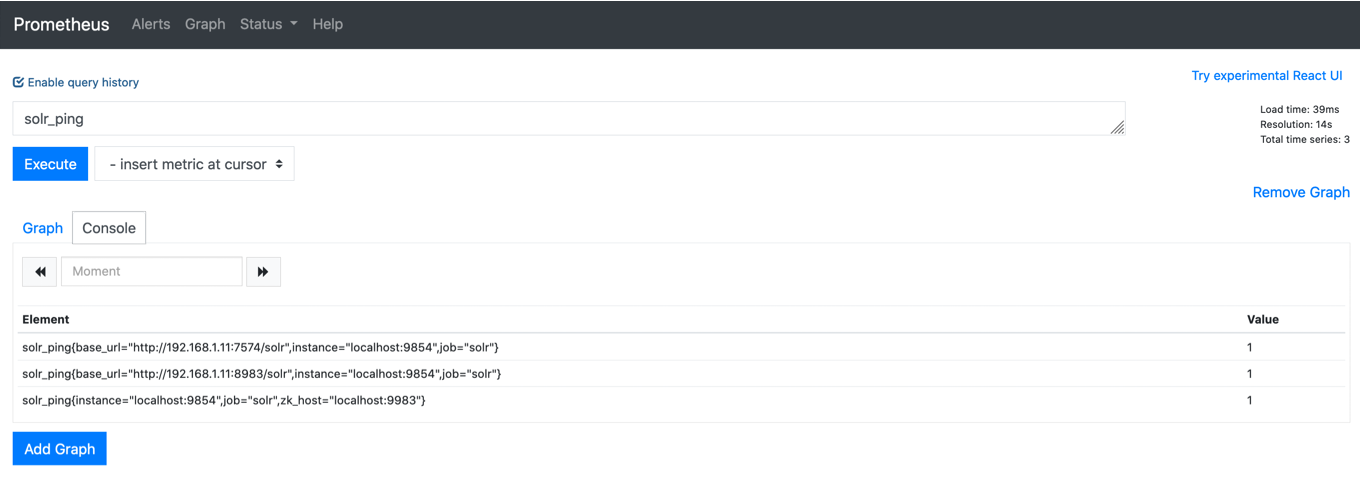
You can test that the Prometheus server, solr-exporter, and Solr are working together by browsing to http://localhost:9090 and
doing a query for solr_ping metric in the Prometheus GUI:
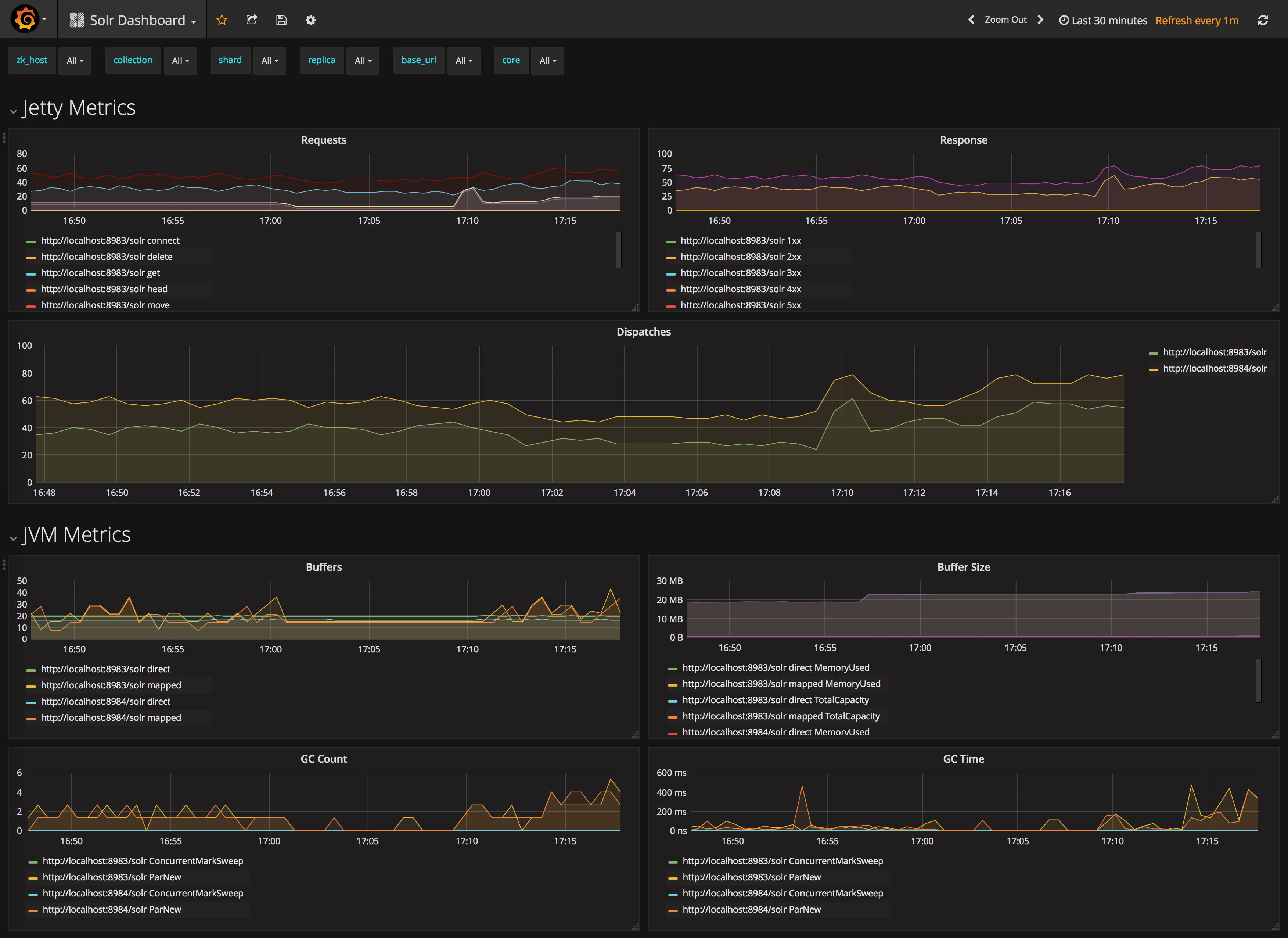
Sample Grafana Dashboard
To use Grafana for visualization, it must be downloaded and deployed separately. More information can be found on the Grafana Documentation site. Grafana consumes data from many sources, including the Prometheus server that you previously set up.
A Grafana sample dashboard is provided in the following JSON file: prometheus-exporter/conf/grafana-solr-dashboard.json.
You can place this with your other Grafana dashboard configurations and modify it as necessary depending on any customization you’ve done for the solr-exporter configuration.
You can directly import the Solr dashboard via grafana.com by using the Import function with the dashboard id 12456.
|
This screenshot shows what it might look like: