Matrices and Matrix Math
Matrices are used as both inputs and outputs of many mathematical functions. This section of the user guide covers the basics of matrix creation, manipulation and matrix math.
Matrices
A matrix can be created with the matrix function.
The matrix function is passed a list of arrays with
each array representing a row in the matrix.
The example below creates a two-by-two matrix.
matrix(array(1, 2),
array(4, 5))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it
responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"return-value": [
[
1,
2
],
[
4,
5
]
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}}Row and Column Labels
A matrix can have column and rows and labels.
The functions
setRowLabels, setColumnLabels, getRowLabels, and getColumnLabels
can be used to set and get the labels.
The label values are set using string arrays.
The example below sets the row and column labels. In other sections of the user guide examples are shown where functions return matrices with the labels already set.
Below is a simple example of setting and getting row and column labels on a matrix.
let(echo="d, e",
a=matrix(array(1, 2),
array(4, 5)),
b=setRowLabels(a, array("rowA", "rowB")),
c=setColumnLabels(b, array("colA", "colB")),
d=getRowLabels(c),
e=getColumnLabels(c))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it
responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"d": [
"rowA",
"rowB"
],
"e": [
"colA",
"colB"
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}Visualization
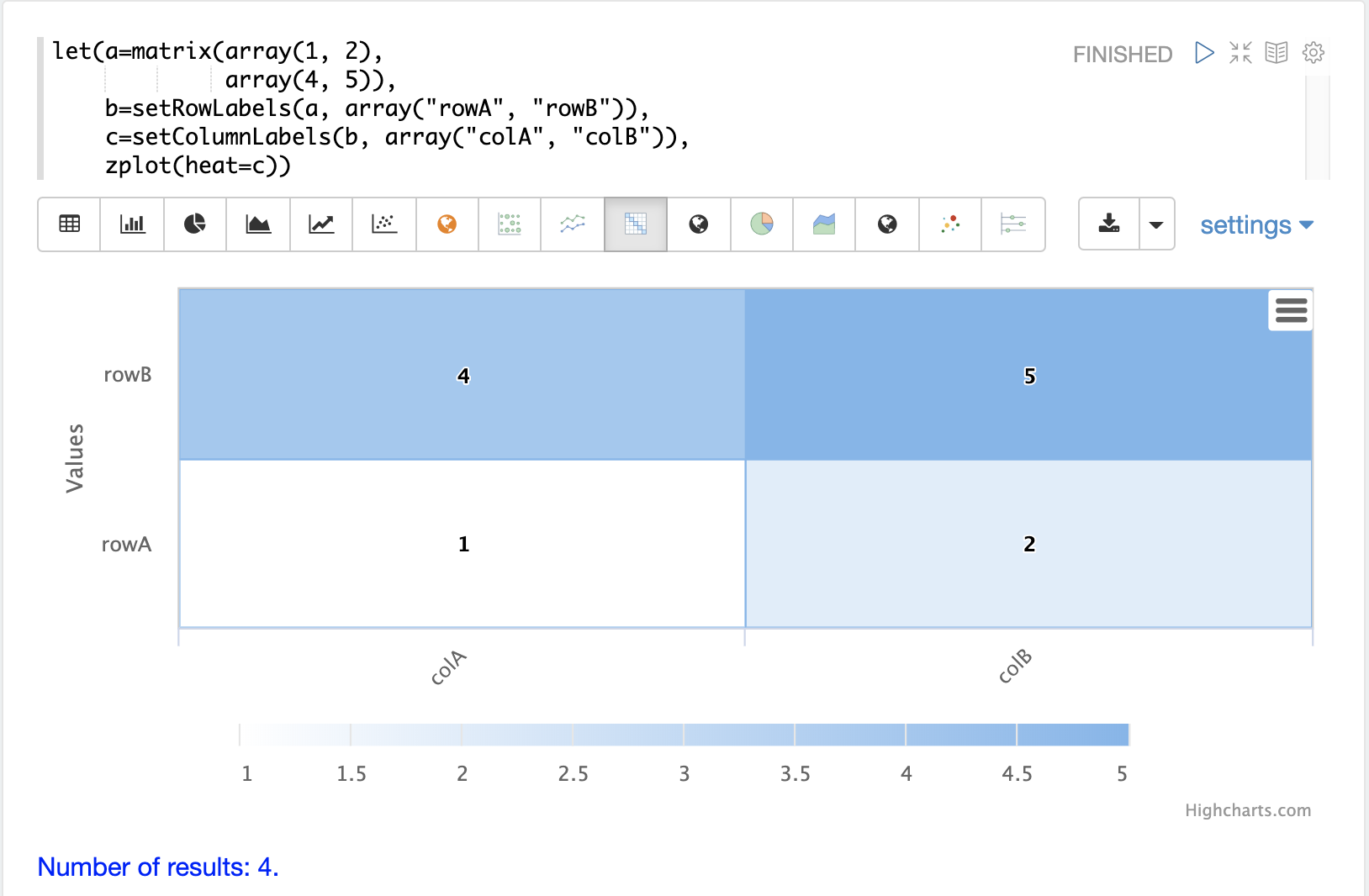
The zplot function can plot matrices as a heat map using the heat named parameter.
Heat maps are powerful visualization tools for displaying correlation and distance matrices described later in the guide.
The example below shows a 2x2 matrix visualized using the heat map
visualization in Apache Zeppelin.
| In the visualization below the rows are read from the bottom up, which is a common convention for heat maps. |
Accessing Rows and Columns
The rows and columns of a matrix can be accessed using the rowAt
and colAt functions.
The example below creates a 2 by 2 matrix and returns the second column of the matrix. Notice that the matrix is passed variables in this example rather than directly passed a list of arrays.
let(a=array(1, 2),
b=array(4, 5),
c=matrix(a, b),
d=colAt(c, 1))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it
responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"d": [
2,
5
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}Matrix Attributes
A matrix can also have an arbitrary set of named attributes associated
with it.
Certain functions, such as the termVectors function,
return matrices that contain attributes that describe data in the matrix.
Attributes can be retrieved by name using the getAttribute function and
the entire attribute map can be returned using the getAttributes
function.
Matrix Dimensions
The dimensions of a matrix can be determined using the
rowCount and columnCount functions.
The example below retrieves the dimensions of a matrix.
let(echo="b,c",
a=matrix(array(1, 2, 3),
array(4, 5, 6)),
b=rowCount(a),
c=columnCount(a))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it
responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"b": 2,
"c": 3
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}Matrix Transposition
A matrix can be transposed
using the transpose function.
An example of matrix transposition is shown below:
let(a=matrix(array(1, 2),
array(4, 5)),
b=transpose(a))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it
responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"b": [
[
1,
4
],
[
2,
5
]
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 24
}
]
}
}Matrix Summations
The rows and columns of a matrix can be summed with the sumRows and sumColumns functions.
Below is an example of the sumRows function which returns an
array with the sum of each row.
let(a=matrix(array(1, 2, 3),
array(4, 5, 6)),
b=sumRows(a))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it
responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"b": [
6,
15
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 2
}
]
}
}The grandSum function returns the sum of all values in the matrix.
Below is an example of the grandSum function:
let(a=matrix(array(1, 2, 3),
array(4, 5, 6)),
b=grandSum(a))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it
responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"b": 21
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}Scalar Matrix Math
The same scalar math functions that apply to vectors can also be applied to matrices: scalarAdd, scalarSubtract,
scalarMultiply, scalarDivide.
Below is an example of the scalarAdd function which adds a scalar value to each element in a matrix.
let(a=matrix(array(1, 2),
array(4, 5)),
b=scalarAdd(10, a))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"b": [
[
11,
12
],
[
14,
15
]
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}Matrix Addition and Subtraction
Two matrices can be added and subtracted using the ebeAdd and ebeSubtract functions,
which perform element-by-element addition
and subtraction of matrices.
Below is a simple example of an element-by-element addition using ebeAdd of a matrix by itself:
let(a=matrix(array(1, 2),
array(4, 5)),
b=ebeAdd(a, a))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"b": [
[
2,
4
],
[
8,
10
]
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}Matrix Multiplication
Matrix multiplication can be accomplished using the matrixMult function.
Below is a simple example of matrix multiplication:
let(a=matrix(array(1, 2),
array(4, 5)),
b=matrix(array(11, 12),
array(14, 15)),
c=matrixMult(a, b))When this expression is sent to the /stream handler it
responds with:
{
"result-set": {
"docs": [
{
"c": [
[
39,
42
],
[
114,
123
]
]
},
{
"EOF": true,
"RESPONSE_TIME": 0
}
]
}
}