Configuring Logging
Solr logs are a key way to know what’s happening in the system. There are several ways to adjust the default logging configuration.
Temporary Logging Settings
There are several ways to temporarily change log levels when needed.
Logging Screen
You can temporarily change the amount of logging output by Solr using the Admin UI. Select the Logging] link in the left-hand menu.
Note that log levels will also be reset on next Solr restart.
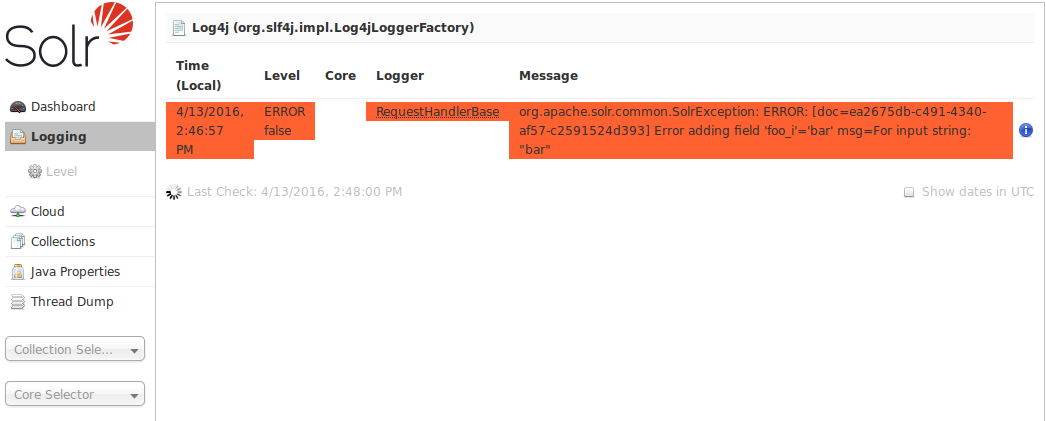
This part of the Admin Web interface allows you to set the logging level for many different log categories. Fortunately, any categories that are unset will have the logging level of its parent. This makes it possible to change many categories at once by adjusting the logging level of their parent.
When you select menu:Logging[Level], you see the following menu:
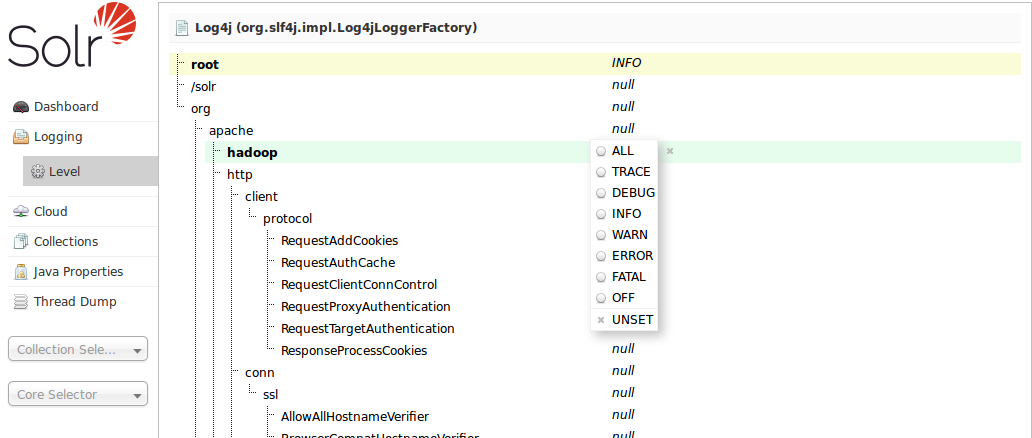
Solr classes are shown in the left column in a directory tree structure representing the classpath. The current level is shown in the right column.
Directories are shown with their current logging levels. A row highlighted in yellow indicates that the class currently has logging enabled. The Log Level Menu floats over these. To set a log level for a particular directory, click the current level in the right column and the Log Level Menu will appear. Select the button next to your desired log level.
The log level change will be distributed to all nodes in the cluster.
The possible log levels are as follows:
| Level | Result |
|---|---|
ALL |
Reports everything. |
TRACE |
Reports everything but the least important messages. |
DEBUG |
Reports configuration errors. |
INFO |
Reports everything but normal status. |
WARN |
Reports all warnings. |
ERROR |
Reports only the most severe warnings. |
FATAL |
Reports only fatal events. |
OFF |
Turns off logging. |
UNSET |
Removes the previous log setting. |
Multiple settings at one time are allowed.
Log Level API
There is also a way of sending REST commands to the admin/info/logging endpoint to do the same.
Example:
-
V1 API
-
V2 API
curl -X GET "http://localhost:8983/solr/admin/info/logging?set=root:WARN"curl -X PUT http://localhost:8983/api/node/logging/levels -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '
[
{"logger": "root", "level": "WARN"}
]
'Choosing Log Level at Startup
You can temporarily choose a different logging level as you start Solr. There are two ways:
The first way is to set the SOLR_LOG_LEVEL environment variable before you start Solr, or place the same variable in bin/solr.in.sh or bin/solr.in.cmd.
The variable must contain an uppercase string with a supported log level (see above).
The second way is to start Solr with the -v or -q options, see Solr Control Script Reference for details. Examples:
# Start with detailed (DEBUG) logging
bin/solr start -f --verbose
# Start with quiet (WARN) logging
bin/solr start -f --quietPermanent Logging Settings
Solr uses Log4J version 2.21.0 for logging which is configured using server/resources/log4j2.xml.
Take a moment to inspect the contents of the log4j2.xml file so that you are familiar with its structure.
By default, Solr log messages will be written to SOLR_LOGS_DIR/solr.log.
The format of the log messages can be changed by modifying the pattern used in the <PatternLayout/>, or by changing the layout implementation — e.g., a <JsonTemplateLayout/> can be used to configure JSON formatted log files.
When you’re ready to deploy Solr in production, set the variable SOLR_LOGS_DIR to the location where you want Solr to write log files, such as /var/solr/logs.
You may also want to tweak log4j2.xml.
Note that if you installed Solr as a service using the instructions provided in Taking Solr to Production, then see /var/solr/log4j2.xml instead of the default server/resources version.
When starting Solr in the foreground (-f option), all logs will be sent to the console, in addition to solr.log.
When starting Solr in the background, it will write all stdout and stderr output to a log file in solr-<port>-console.log, and automatically disable the CONSOLE logger configured in log4j2.xml, having the same effect as if you removed the CONSOLE appender from the rootLogger manually.
Also, in log4j2.xml if the default log rotation size threshold of 32MB is too small for production servers then you should increase it to a larger value (such as 100MB or more).
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="100 MB"/>Java Garbage Collection logs are rotated by the JVM when size hits 20M, for a max of 9 generations.
On every startup or restart of Solr, log4j2 performs log rotation.
Logging Slow Queries
For high-volume search applications, logging every query can generate a large amount of logs and, depending on the volume, potentially impact performance. If you mine these logs for additional insights into your application, then logging every query request may be useful.
On the other hand, if you’re only concerned about warnings and error messages related to requests, then you can set the log verbosity to WARN. However, this poses a potential problem in that you won’t know if any queries are slow, as slow queries are still logged at the INFO level.
Solr provides a way to set your log verbosity threshold to WARN and be able to set a latency threshold above which a request is considered "slow" and log that request at the WARN level to help you identify slow queries in your application.
To enable this behavior, configure the <slowQueryThresholdMillis> element in the query section of solrconfig.xml:
<slowQueryThresholdMillis>1000</slowQueryThresholdMillis>Any queries that take longer than the specified threshold will be logged as "slow" queries at the WARN level.
The log file under which you can find all these queries is called solr_slow_requests.log and will be found in your SOLR_LOGS_DIR (see Permanent Logging Settings for more about defining log locations).
Logging Select Request Parameters
In addition to the logging options described above, it’s possible to log only a selected list of request parameters (such as those sent with queries) with an additional request parameter called logParamsList.
See the section on logParamsList Parameter for more information.
Selective Logging on SolrCore
Solr logs all core requests at INFO level using the o.a.s.c.SolrCore.Request. This can be disabled entirely by changing the level of these loggers to WARN or ERROR, or more selectively by using the MarkerFilter on request paths in log4j2.xml.
For example:
<Logger name="org.apache.solr.core.SolrCore.Request" level="info">
<Filters>
<MarkerFilter marker="/get" onMatch="DENY" onMismatch="NEUTRAL"/>
<MarkerFilter marker="/replication" onMatch="DENY" onMismatch="NEUTRAL"/>
</Filters>
</Logger>Request Logging
Every incoming HTTP(s) request is by default logged in the standard NCSA format
in files with name $SOLR_LOG_DIR/<yyyy_mm_dd>.request.log, rolled over daily. By default, 3 days worth of request logs are retained.
You can disable request logging by setting SOLR_REQUESTLOG_ENABLED=false via environment variable or in solr.in.sh/solr.in.cmd.
You can change the number of days to retain by system property -Dsolr.log.requestlog.retaindays.